Infection
Many millions suffer from infections with Hepatitis B Virus, Hepatitis C Virus, as well as the human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). These viral infections can not always be eliminated from our immune system followed by a virus persistence and chronic viral infection. Several components of the immune system fail during establishment of a chronic viral infection. Research on chronic viral infections is critical to better understand the immunology behind these virus infections and the mechanisms for turning an acute infection into a chronic disease. New factors which contribute to fighting a viral infection may be used for future therapeutic regimens.
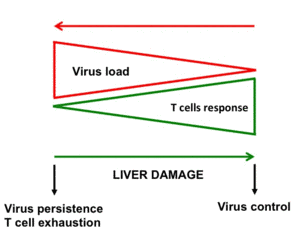
One mechanism which contributed to viral infection is the exhaustion of anti-viral T cells. In particular, T cells loose their function and are no longer able to kill virus infected cells. Consequently, virus infected cells spread the pathogen and establish a chronic viral infection. Our department tries to identify factors that can influence the equilibrium between viral load and T cell immunity.
Anti-viral T cells are not only protective during viral infection but also induce tissue damage by killing virus infected cells. Thus, T cells identify and kill virus infected hepatocytes during viral induced hepatitis. This tissue damage induced chronic liver inflammation during a chronic viral infection. Our department tries to identify factors, which contribute to virus-induced T cell-mediated liver damage.



