Vascular Medicine Working Group
Large artery stiffness
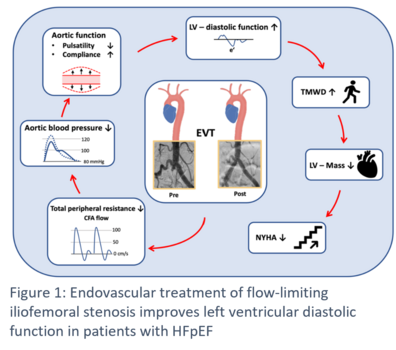
In 2024, the aorta has been recognised as a separate organ, reflecting the important role of the aorta beyond its conduit function. Diseases of the aorta and it's outgoing peripheral arteries also affect end-organ damage, especially the heart, and may contribute to the development of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. The complex interaction between vascular and cardiac function is known as cardiovascular coupling. We aim to investigate the mechanisms of cardiovascular coupling in patients with peripheral arterial disease (Figure 1).
Baasen S, Stern M, Wischmann P, Schremmer J, Sansone R, Spieker M, Wolff G, Bönner F, Quast C, Heiss C, Kelm M, Busch L. Endovascular Treatment of Flow-Limiting Iliofemoral Stenosis Improves Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Patients With HFpEF by Reducing Aortic Pulsatile Load. Circ Heart Fail. 2024 Sep;17(9):e011258. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.123.011258. Epub 2024 Sep 9. PMID: 39247971; PMCID: PMC11398288.
Busch L, Heinen Y, Stern , Wolff G, Özaslan G, Tzetou K, Sansone R, Heiss C, Kelm M. Angioplasty of Flow-Limiting Stenosis Reduces Aortic and Brachial Blood Pressure in Patients With Peripheral Artery Disease. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Jul 20;10(14):e019724. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.019724. Epub 2021 Jul 6. PMID: 34227407; PMCID: PMC8483469.
Schremmer J, Busch L, Baasen S, Heinen Y, Sansone R, Heiss C, Kelm M, Stern M. Chronic PCSK9 inhibitor therapy leads to sustained improvements in endothelial function, arterial stiffness, and microvascular function. Microvasc Res. 2023 Jul;148:104513. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2023.104513. Epub 2023 Mar 3. PMID: 36870561.
Diabetic foot Syndrome
Diabetic foot syndrome is a challenging metabolic disorder. Peripheral artery disease increases the risk of diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) that do not heal and limb amputations. The optimal timing for treating chronic leg artery stenosis using peripheral angioplasty, as well as the role of microbiome composition in diabetic foot ulcers, remain unclear. We have initiated a prospective, randomised, controlled, monocentric trial including individuals with T2D and DFU who are over 18 years of age and have haemodynamically relevant chronic PAD (the PTA-DFS study). The PTA-DFS study aims to improve diagnostic and therapeutic algorithms and risk assessment, and enable the provision of tailored therapies for people with T2D and ischaemic DFU.
Trial Registration Number: NCT06124586.
Venous diseases
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a potentially life-threatening condition. There is no sufficient evidence on the benefits of endovascular treatment. As one of a small number of centres in Europe, we participated in the prospective, multicentre, randomised controlled PEERLESS trial, which compared large-bore mechanical thrombectomy (LBMT) and catheter-directed thrombolysis (CDT) in patients with intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism. We are currently participating in the PEERLESS II study, which compares anticoagulation and LBMT. In addition, we are involved in scientific research related to proximal deep vein thrombosis.
Jaber WA, Gonsalves CF, Stortecky S, Horr S, Pappas O, Gandhi RT, Pereira K, Giri J, Khandhar SJ, Ammar KA, Lasorda DM, Stegman B, Busch L, Dexter DJ 2nd, Azene EM, Daga N, Elmasri F, Kunavarapu CR, Rea ME, Rossi JS, Campbell J, Lindquist J, Raskin A, Smith JC, Tamlyn TM, Hernandez GA, Rali P, Schmidt TR, Bruckel JT, Camacho JC, Li J, Selim S, Toma C, Basra SS, Bergmark BA, Khalsa B, Zlotnick DM, Castle J, O'Connor DJ, Gibson CM; PEERLESS Committees and Investigators*. Large-Bore Mechanical Thrombectomy Versus Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis in the Management of Intermediate-Risk Pulmonary Embolism: Primary Results of the PEERLESS Randomized Controlled Trial. Circulation. 2025 Feb 4;151(5):260-273. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.124.072364. Epub 2024 Oct 29. PMID: 39470698; PMCID: PMC11789609.
Working Groups
- DFU (Head: Dr. med. P. Wischmann)
- Venous Dieseases (Head: Dr. med. P. Wischmann)
- Large Artery Stiffness (Head: Dr. med. S. Baasen)



